Hearing Loss 101
HOME / HEARING LOSS 101
YOU MAY HAVE HEARING LOSS IF YOU…
- need people to repeat themselves or ask others what was said
- experience difficulty understanding what people are saying
- find difficulty following conversations in noisy environments like grocery stores or restaurants
- tend to avoid social situations because it’s hard to hear others
- increase the volume on the television or radio, but those around you say it’s too loud
- experience ringing in the ears
- have been told that you don’t hear well
Who Experiences Hearing Loss?
Approximately 48 million people (about one in six baby boomers) experience hearing loss, and that’s just here in America! Most of the time folks lose their hearing as an unfortunate side-effect of growing older, but it can also be caused by some medical conditions (like diabetes), loud noise, or injury/damage.
Most of our patients have found that hearing loss occurs very slowly over a long period of time. Throughout the years, folks have simply “learned to live” with the changes by turning up the radio or television, asking others to repeat what was said, or letting conversations slip by. When hearing is reduced some people start avoiding social situations because they feel embarrassed or hate constantly asking others to repeat themselves. Some might even give up beloved activities like volunteering, going to church, or even participating in family get-togethers because it’s too difficult. But you don’t have to change your life - most hearing loss is treatable!
Types of Hearing Loss
There are four main types of hearing loss; our specialists will help identify which type you are experiencing and the degree of severity. This is the first step to improving your hearing. A hearing test will identify any hearing loss you may have and the extent.
Conductive
This type of hearing loss may be temporary and can often be resolved through medication, brief procedure, or through surgery (rarely).
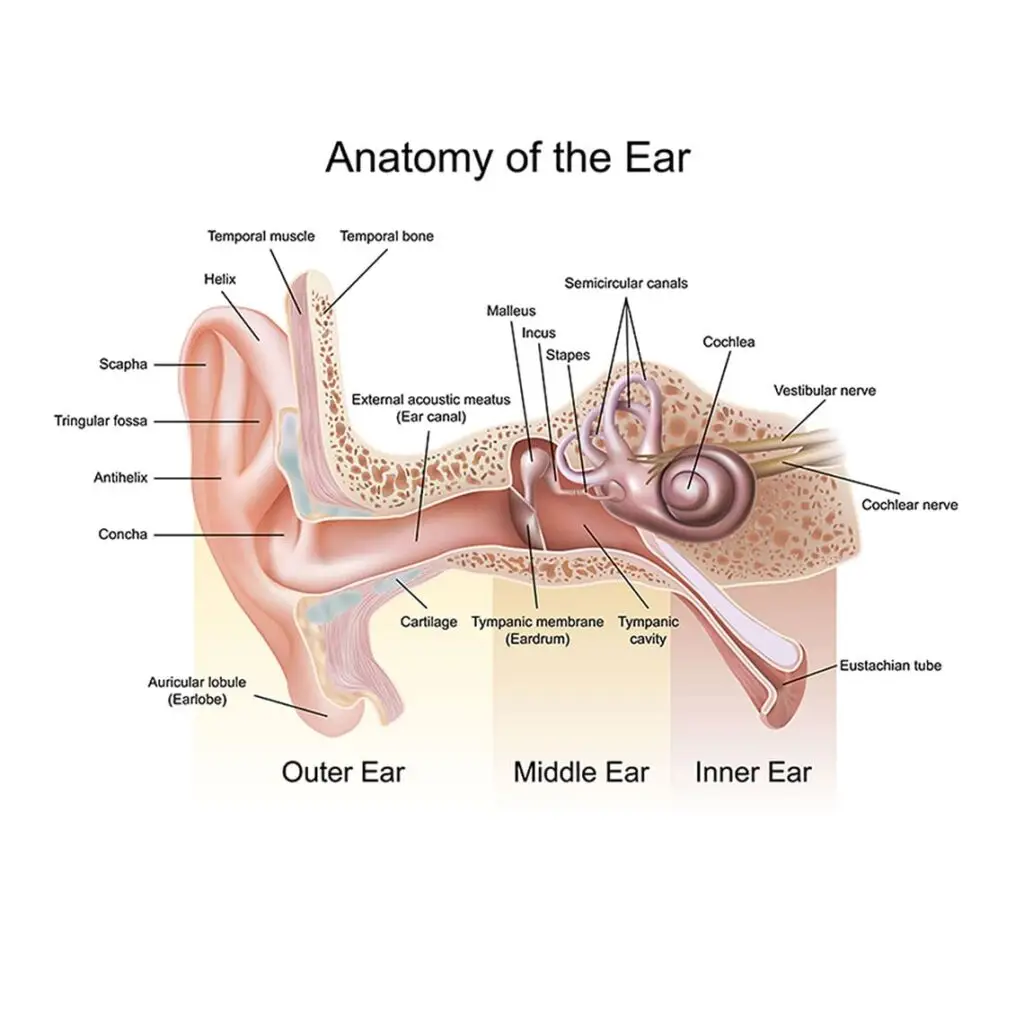
Sensorineural
There are tiny hairs found in the cochlea, and when they are damaged or missing, sensorineural hearing loss can occur. Surgery or hearing aids are the only solutions.
Mixed
Mixed hearing loss occurs when someone experiences both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. It is usually treated with hearing aids but can also be treated in combination with surgery, a brief procedure, or medication.
Central
Central hearing loss is the result of diseases to the central nervous system (or after a stroke). A type of therapy called auditory rehabilitation is usually necessary after this type of hearing loss has occurred.
IT’S TIME TO GET BACK TO YOUR LIFE AND ENJOY THE BENEFITS OF BETTER HEARING
Hearing isn’t just about participating in conversation; good hearing plays a role in information processing, brain function, and self-confidence. The sooner you assess your hearing loss and work on a solution, the sooner you can get back to normal.